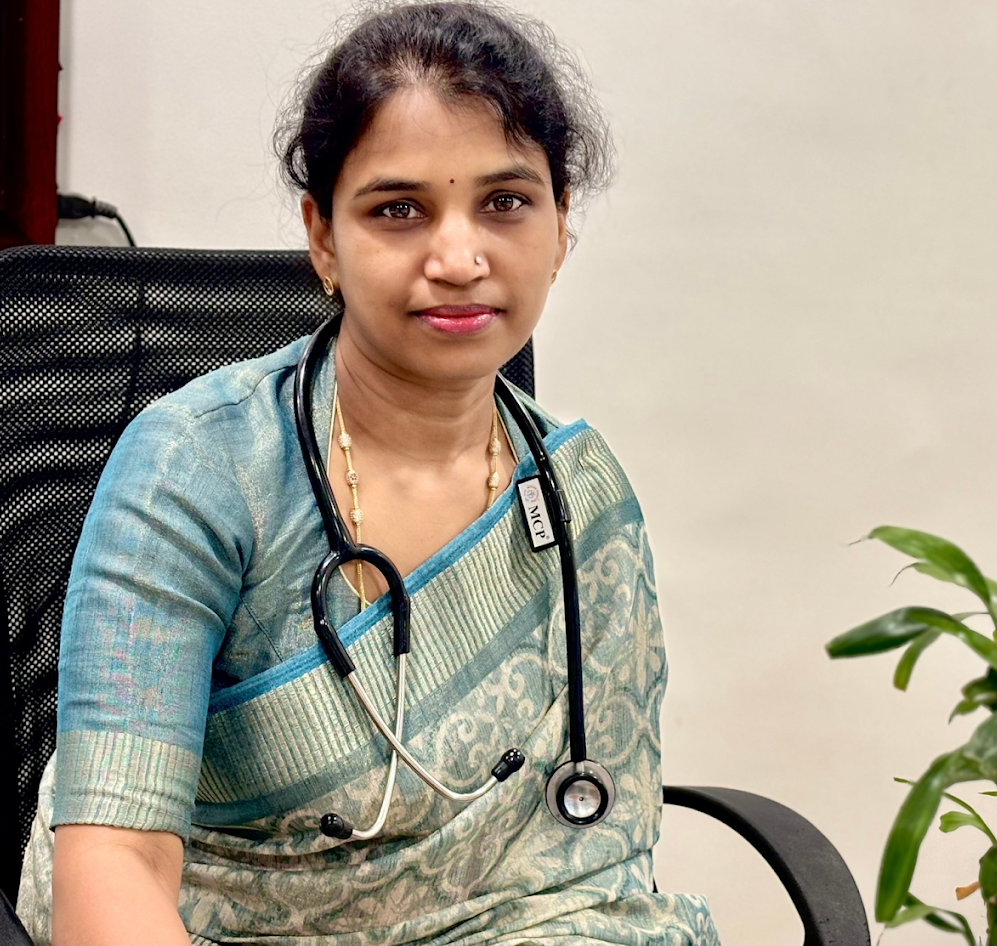
Diabetes in Pregnancy (GDM)
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) can present challenges during pregnancy, but appropriate treatment can help manage the condition effectively. Treatment options for GDM typically involve dietary modifications, physical activity, monitoring blood glucose levels, and, in some cases, medication. A key aspect of treatment is maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Healthcare providers may recommend a personalized meal plan that focuses on balanced nutrition and portion control to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity is also beneficial for managing GDM as it helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Monitoring blood glucose levels through regular testing allows for adjustments in diet, exercise, or medication as needed to maintain optimal control. In cases where lifestyle modifications are insufficient, insulin therapy may be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels. The goal of treatment for GDM is to achieve optimal maternal and fetal outcomes while minimizing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy.
Benefits of Gestational Diabetes Treatment
- Reduction in the risk of macrosomia (large birth weight) in newborns, lowering the likelihood of birth complications.
- Prevention of neonatal hypoglycemia, which can occur due to high maternal blood glucose levels during pregnancy.
- Lowered risk of preeclampsia and other pregnancy-related complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
- Improved maternal health outcomes, including reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Enhanced monitoring and management of maternal and fetal well-being throughout the pregnancy.
- Promotion of healthy lifestyle habits that can benefit both the mother and the baby beyond the pregnancy.

.jpg)




