Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
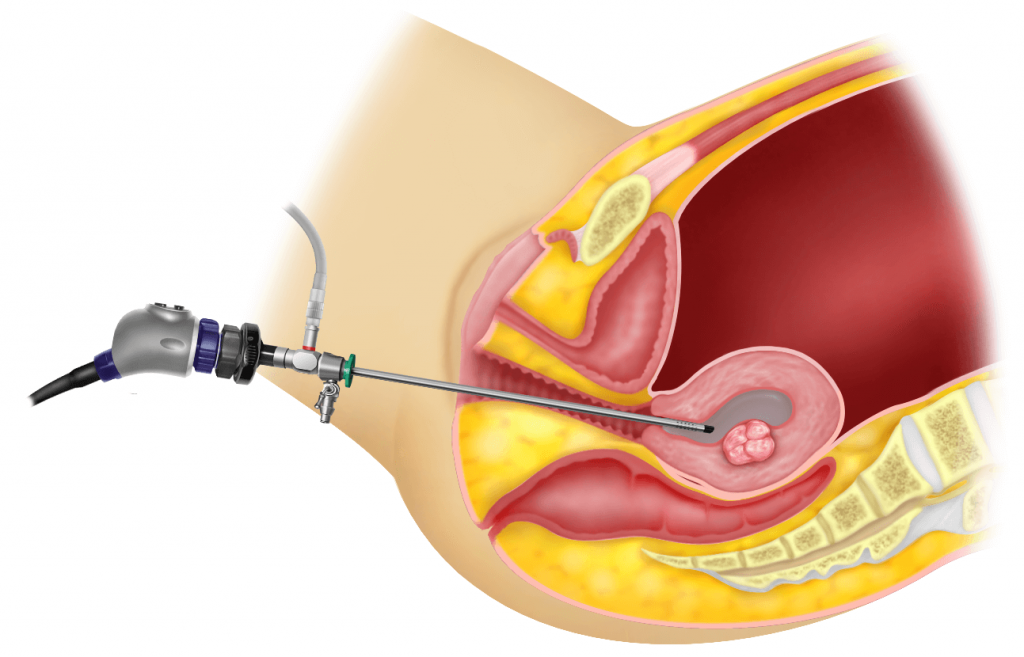
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to examine the inside of the uterus. It involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (hysteroscope) through the cervix into the uterus, allowing healthcare providers to visually inspect the uterine cavity and identify any abnormalities or conditions that may be causing symptoms. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is commonly performed to investigate issues such as abnormal uterine bleeding, recurrent miscarriages, or infertility.
The procedure is typically performed in an outpatient setting and may be done with local anesthesia or sedation to minimize discomfort. During the hysteroscopy, the healthcare provider can take biopsies or samples of tissue for further examination if necessary. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is considered a safe and effective diagnostic tool with minimal risks and complications. It provides valuable information that can help guide treatment decisions and improve outcomes for women experiencing gynecological issues.
Benefits of Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
- Allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity, enabling healthcare providers to identify and diagnose various uterine conditions or abnormalities.
- Minimally invasive procedure with little to no recovery time, allowing women to resume their normal activities shortly after the procedure.
- Can be used to investigate the cause of symptoms such as abnormal uterine bleeding, recurrent miscarriages, or unexplained infertility.
- May help detect and diagnose conditions such as fibroids, polyps, adhesions, or uterine septum that may contribute to gynecological issues.
- Provides valuable information that can guide treatment decisions and help healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans for patients.
- Allows for the collection of tissue samples (biopsies) for further examination, if necessary, to confirm a diagnosis or rule out other potential causes of symptoms.
- Generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with minimal risks of complications such as infection or injury to the uterus.
- Can be performed in conjunction with other procedures, such as hysteroscopic surgery, to treat identified abnormalities or conditions and improve reproductive health.